We will catalogue and test use of “side-lined” or “underutilised” native plants to restore degraded soils in Ethiopia, characterising impacts on biodiversity, poverty alleviation, and climate adaptation and mitigation.
Challenge
Ethiopia faces the urgent challenge of restoring soil health while strengthening biodiversity, climate resilience and rural livelihoods. Despite the wealth of underutilized plant species in Ethiopia, such as drought-tolerant local crops, resilient perennials, nutrient-enhancing legumes, and bank-stabilizing vegetation, their potential remains largely untapped. Harnessing these species requires transformative land management that integrates indigenous practices with modern science.
The challenge is to build tools that capture traditional knowledge, new measurements and systems-based insights into soil, water, food, climate and farmer wellbeing. These tools must be adaptable, practical and co-designed with smallholder farmers, who are the primary agents of change, ensuring solutions are attractive, usable and widely disseminated. At the same time, policymakers need concise, actionable information to enable supportive frameworks. Achieving this integration across diverse stakeholders will determine whether Ethiopia can pioneer scalable approaches to soil restoration and resilience, offering lessons applicable across Sub-Saharan Africa.
Insight
Our project addresses the challenge of restoring soil health in Ethiopia by systematically cataloguing and characterising underutilised plant species with proven potential across Sub-Saharan Africa. Through systematic review, meta-analysis and systems modelling, we will build a comprehensive catalogue of species, enriched by community engagement in the Bilate catchment to ensure local relevance. Laboratory and field studies will then characterise their impacts on soil health, water retention, erosion control, crop productivity, climate adaptation, biodiversity and livelihoods. This integrated approach combines scientific expertise in microbial and plant diversity, dynamic simulation modelling, and socio-economic analysis with traditional knowledge and farmer perspectives.
The expected impact is a set of co-designed tools and dissemination methods, ranging from mobile apps and decision-support systems to paper-based formats in local languages, that empower smallholder farmers and inform policymakers. By evaluating dissemination strategies and framing training toolkits, we aim to ensure uptake and sustained use. Insights gained to date highlight the importance of combining indigenous practices with scientific studies and modelling to capture system-wide interactions between soil, water, biodiversity and livelihoods. This participatory, systems-based approach will generate scalable solutions for soil restoration and resilience, with lessons applicable across Sub-Saharan Africa.
Collaboration
The project is led by the University of Aberdeen, bringing multidisciplinary expertise across soil science, biodiversity, economics and climate resilience. Jo Smith (soil modelling) and Georgios Leontidis (machine learning) contribute to cataloguing under-utilised species, while Hawassa University contribute expertise in conservation and community engagement (led by Awdenegest Moges). From the University of Aberdeen, Paul Hallett (soil health, erosion), David Burslem (tropical biodiversity), Cecile Gubry Rangin (microbial ecology), Pete Smith (global change) and Euan Phimister (rural economics) bring expertise to characterise impacts on soil health, biodiversity, climate resilience and livelihoods.
Work led by Wolde Bori (International Water Management Institute) adds strengths in soil stabilisation, hydrology, irrigation, food production and gender inclusion. Getahun Yakob (Central Ethiopia Institute of Agricultural Research, Ethiopia), brings expertise in agroforestry and soil management, supporting field sites, and leading dissemination and community engagement. Together, these partnerships ensure robust, interdisciplinary delivery and impact.
Professor Jo Smith
Jo Smith is Professor of Soil Organic Matter and Nutrient Modelling at the University of Aberdeen, specialising in systems modelling and sustainable land management. She has extensive experience leading interdisciplinary projects on agriculture, climate resilience and ecosystem services, with a strong track record of collaboration across international research networks.
Her work integrates biophysical modelling with socio-economic perspectives to assess impacts of land use change, organic waste recycling and underutilised plants on soil health, biodiversity, and livelihoods. As Principal Investigator, she will coordinate project delivery, ensuring robust scientific outputs and effective dissemination to global policy and practitioner communities.
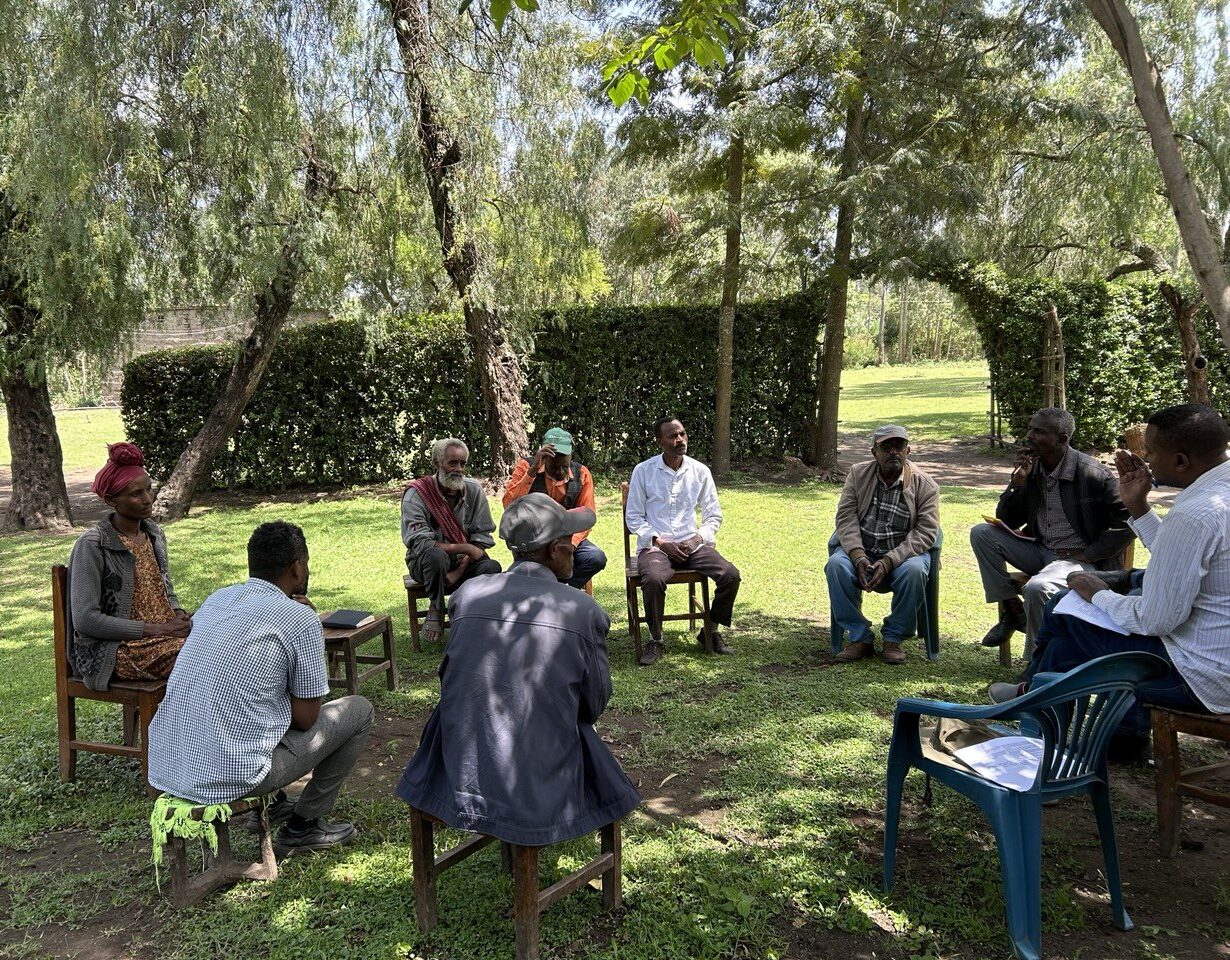
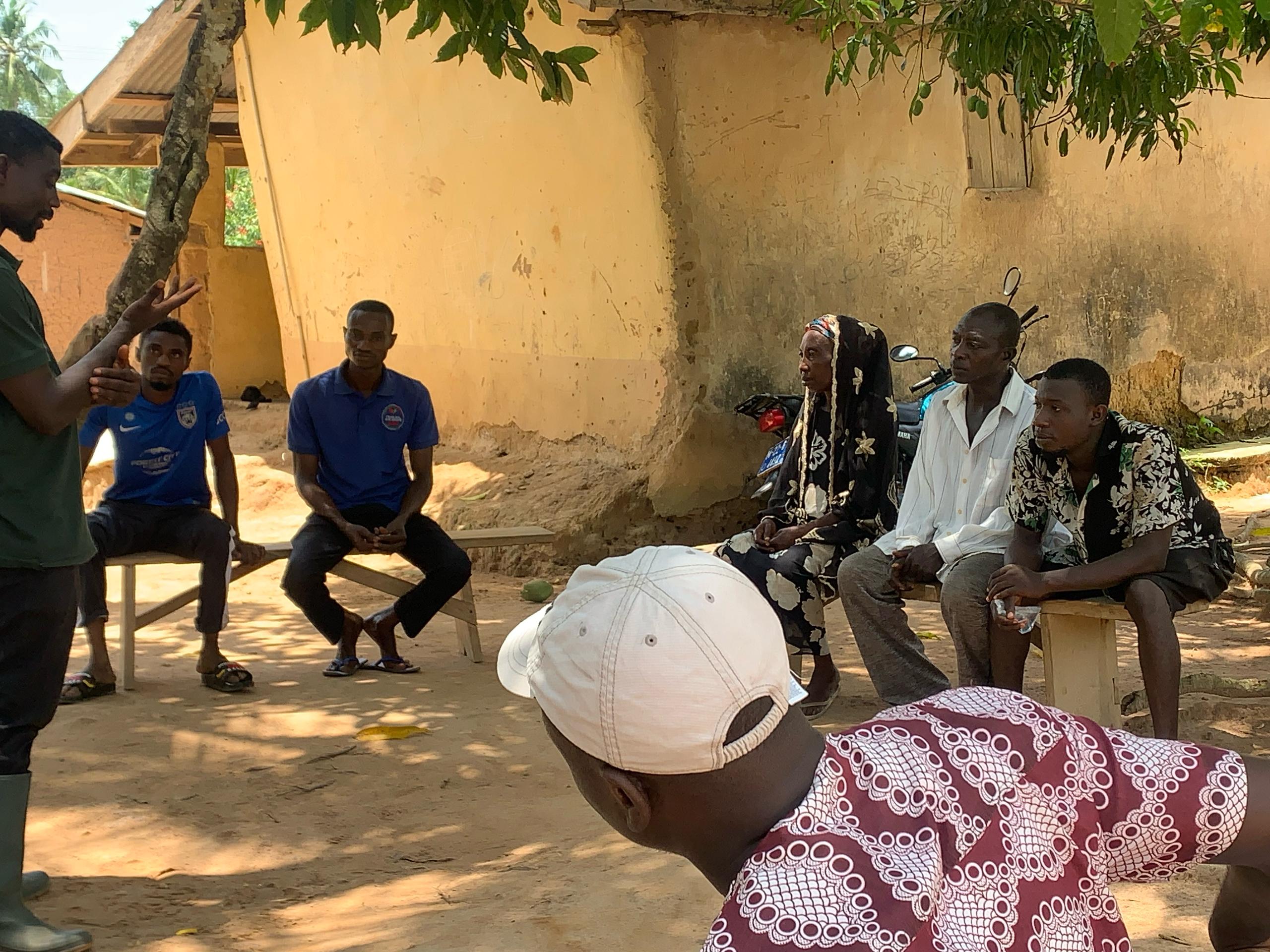
Photo Credits: 1) Scientists from the project and participating farmers sit together in an outdoor circle, engaged in discussion. Photo credit: Prof. Awdenegest Moges. Header Image: Photography (detail): A. Davey