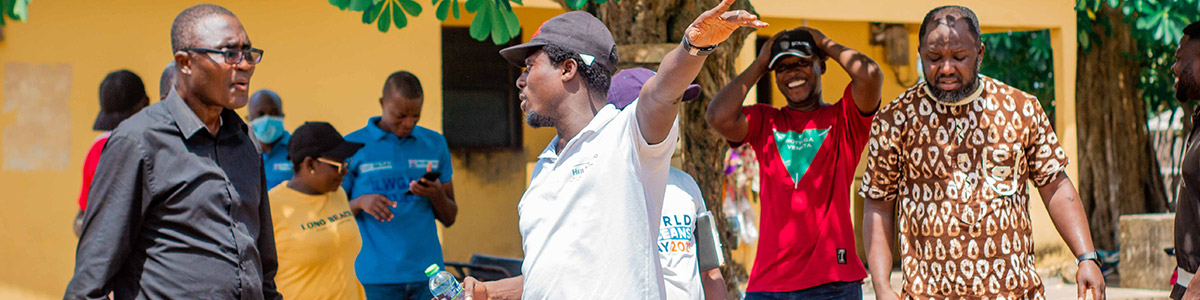People, Nature, and Resilience: Launching ILWGAWS in Ghana’s Coastal Wetlands
The Integrated Land and Water Management of the Greater Amanzule Wetland System (ILWGAWS) is an environmental conservation initiative focused on conserving and restoring biodiversity within the Greater Amanzule Wetland, located in Ghana’s Western Region. This critical ecological zone spans over 50,000 hectares and plays a vital role in supporting biodiversity, enhancing coastal resilience, and sustaining local livelihoods.
However, the region faces significant challenges due to increasing pressures such as climate change, changes in land use and land cover, and hydrological and socio-economic dynamics. Funded by the UK Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA) through the Global Centre on Biodiversity for Climate (GCBC), the project is being implemented by the University of Education, Winneba (UEW), in partnership with Hen Mpoano and the CSIR-Water Research Institute.
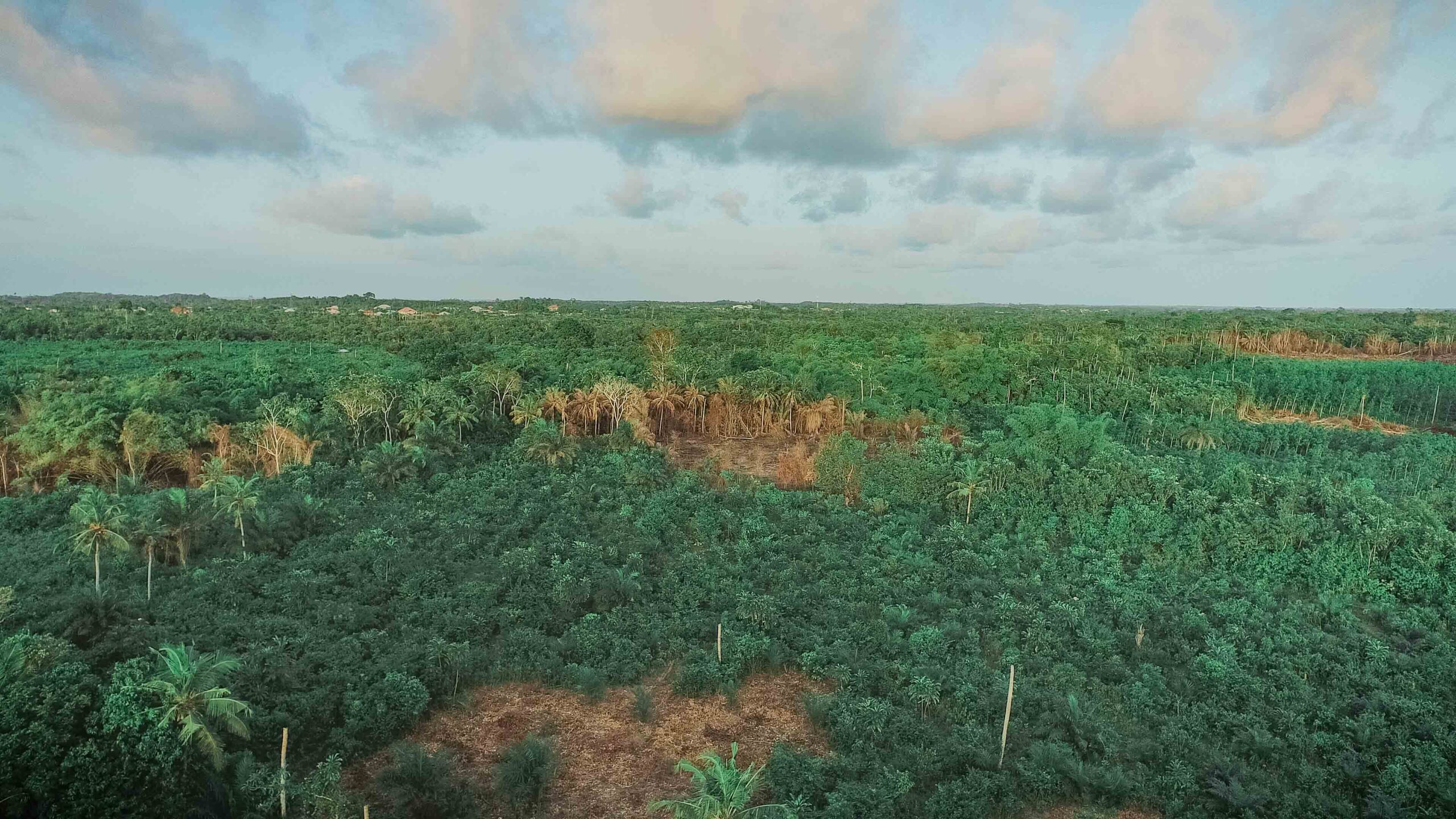
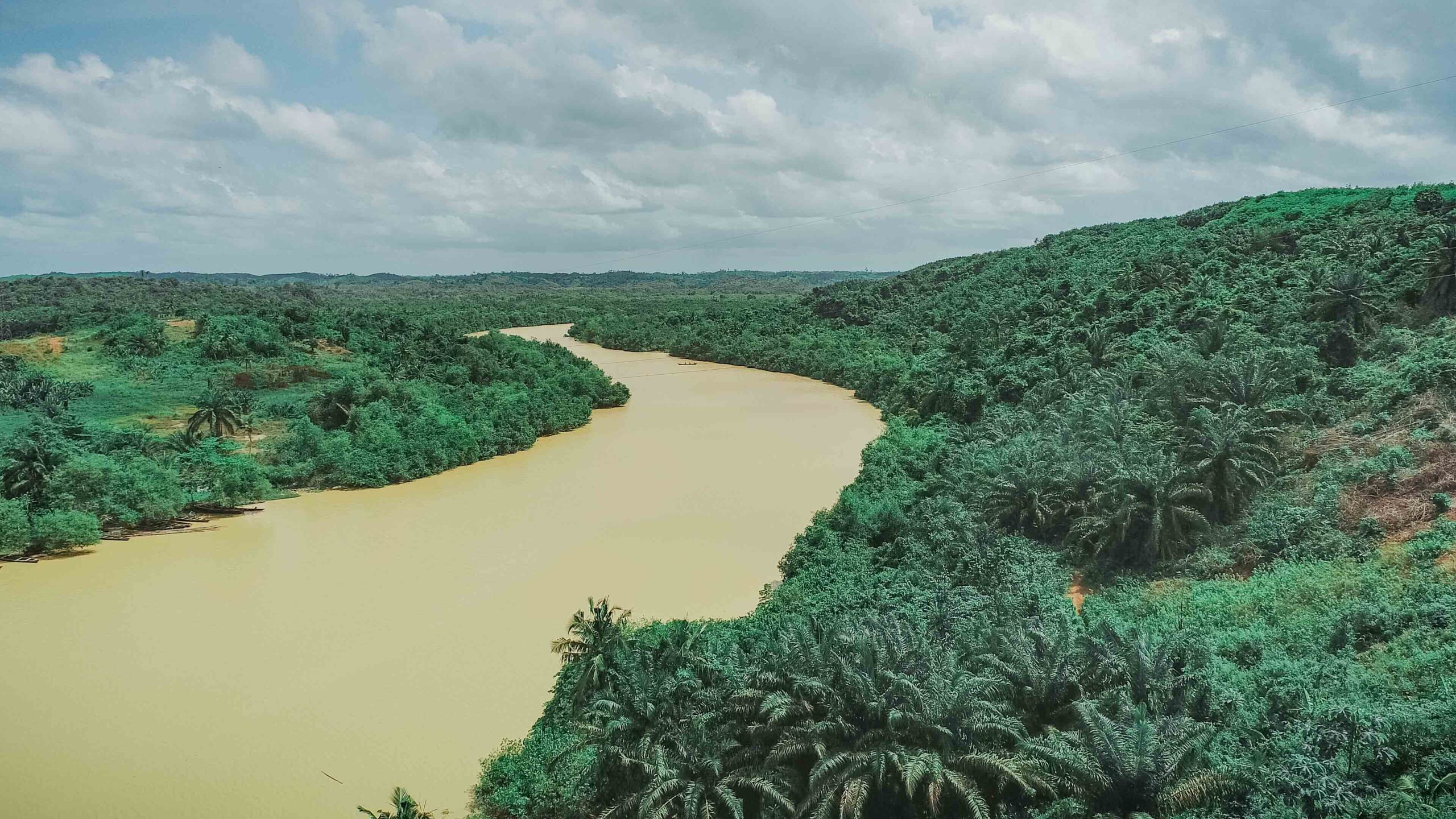
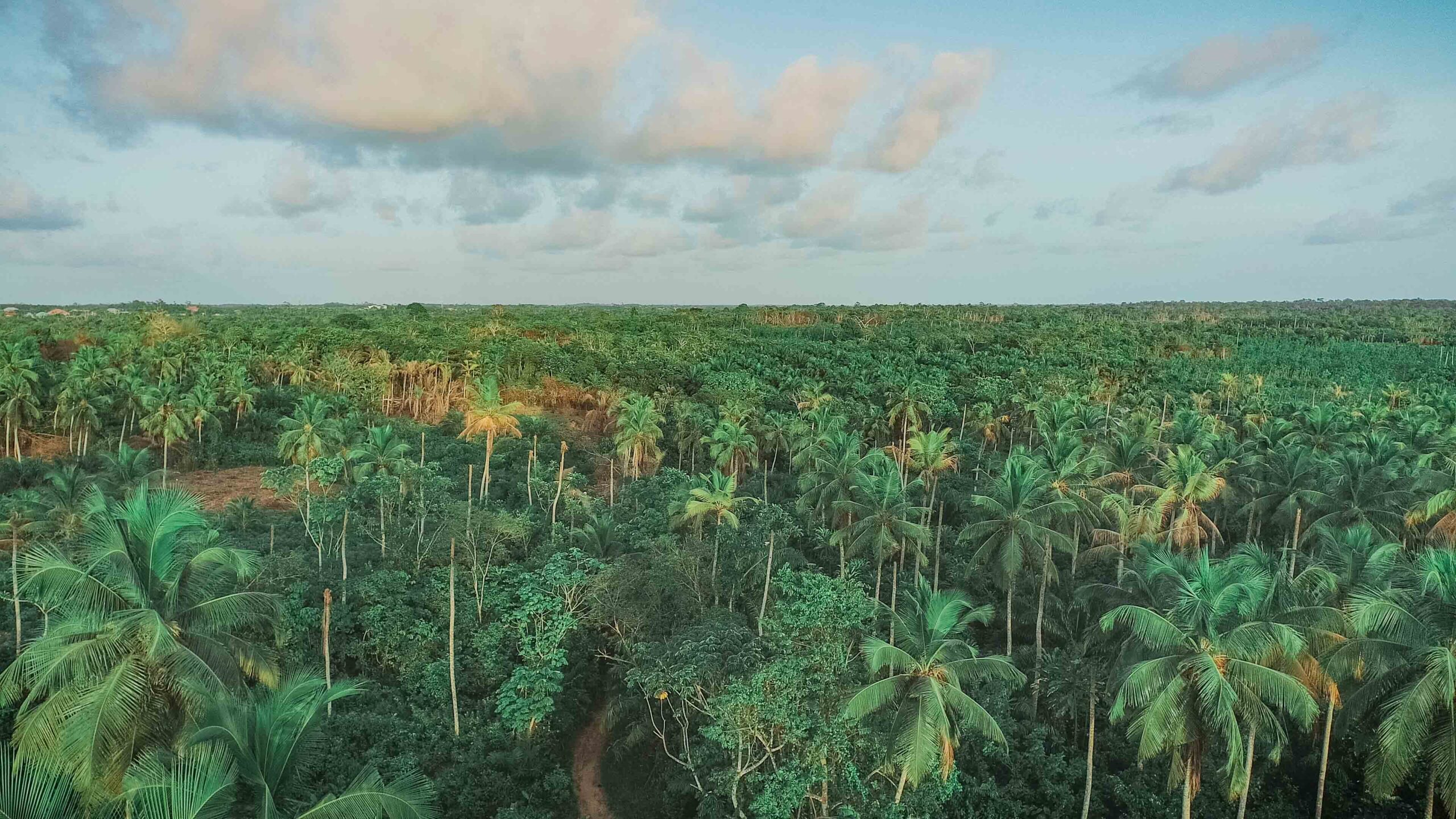
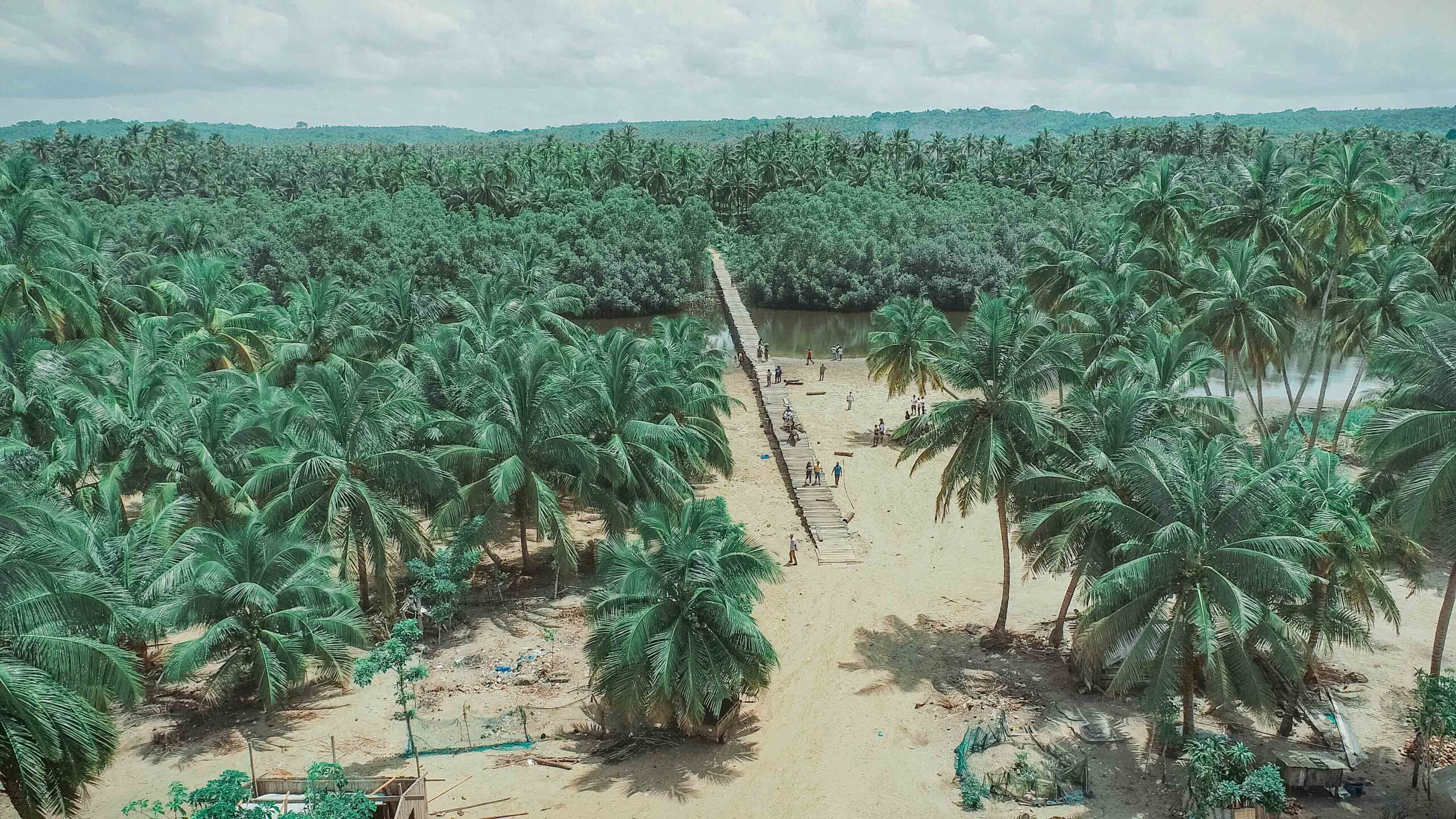
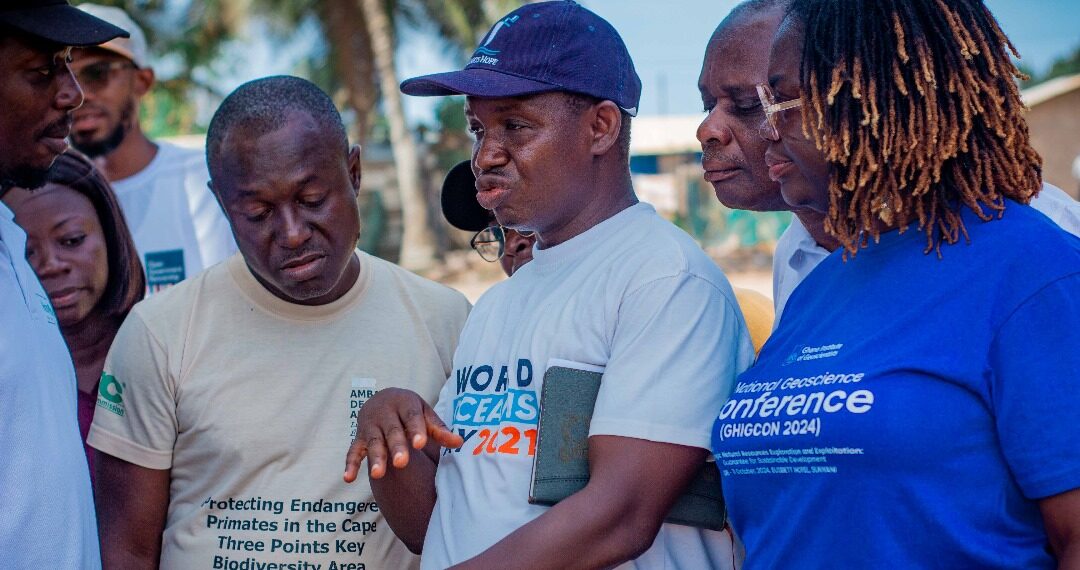
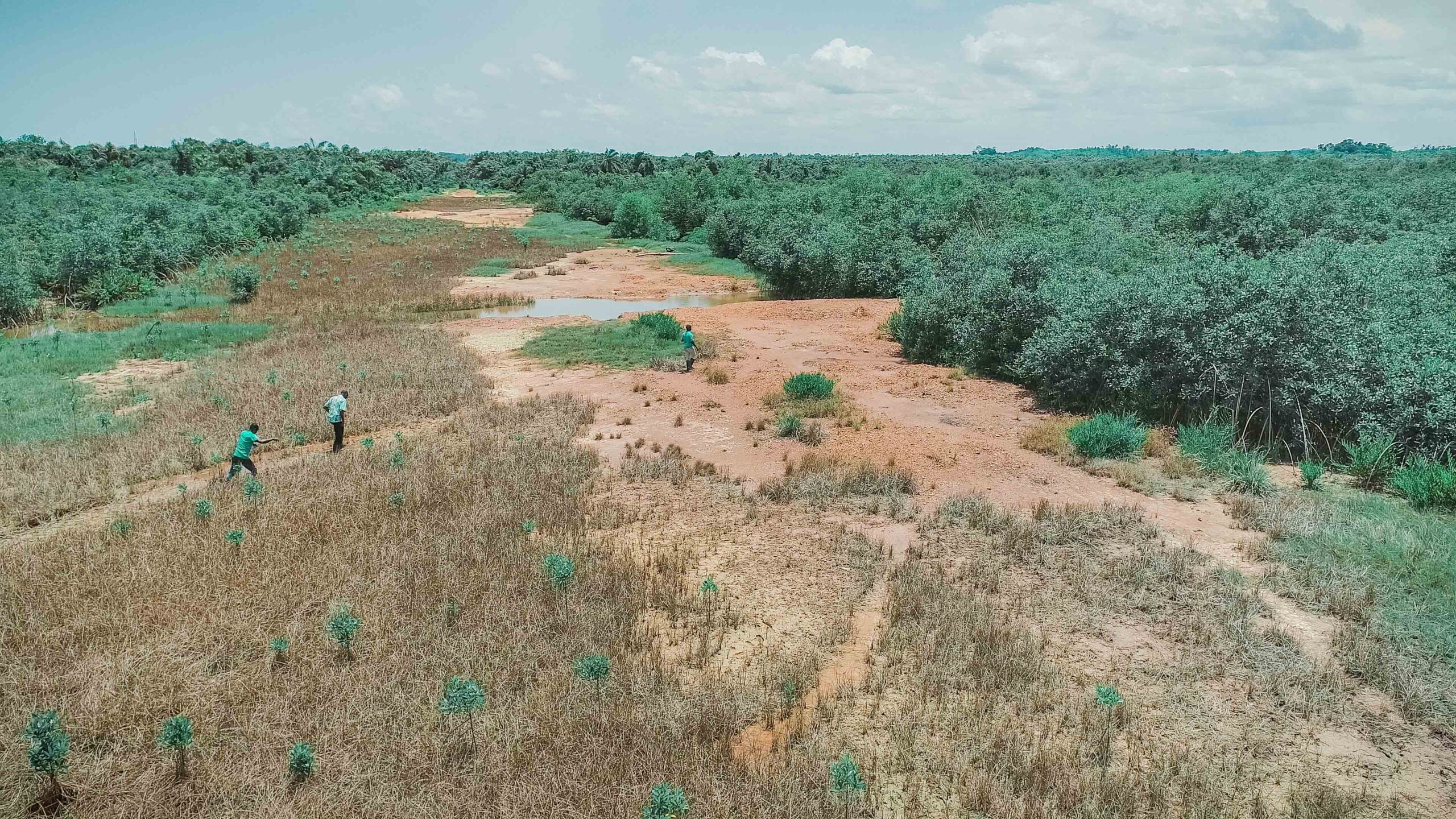












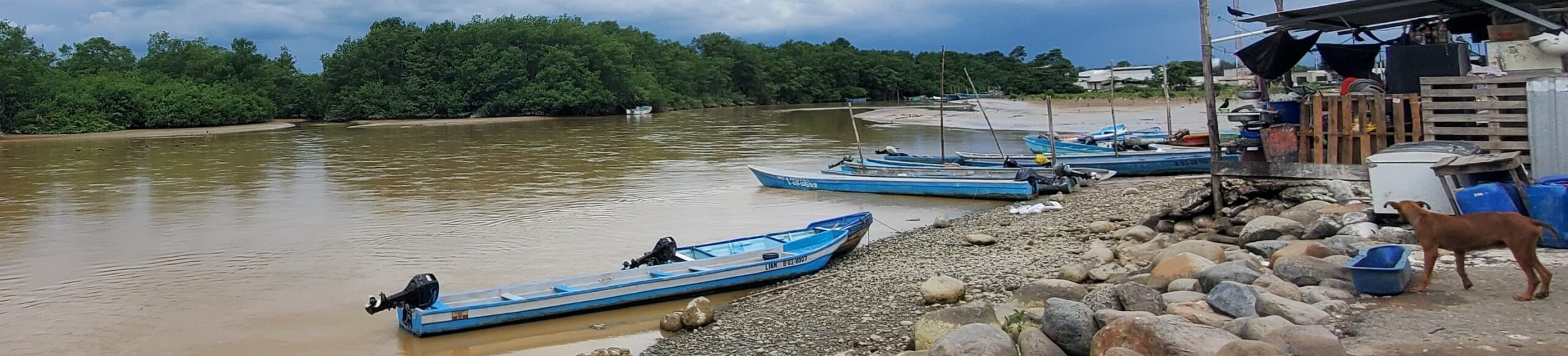
Images depict deforestation, polluted rivers, and degraded mangroves in Ghana’s Amanzule Wetland System, captured during a reconnaissance visit by participants of the inaugural ILWGAWS workshop. Images courtesy of the ILWGAWS media team.
Project Launch: A Vision for People and Nature
The ILWGAWS project launched in the Jomoro Municipality of the Western Region of Ghana, marking a critical step in the project’s broader commitment to environmental sustainability and biodiversity conservation. Led by Dr. Adams Osman, the ILWGAWS project adopts a multidisciplinary, community-led approach that integrates scientific research with local knowledge systems to promote long-term environmental health and economic well-being for communities living within the wetland landscape.
The launch brought together a diverse group of stakeholders, including government officials, traditional leaders, community members, development partners, researchers, and civil society organisations. Professor Stephen Jobson Mitchual, Vice-Chancellor of UEW, delivered a compelling keynote address, emphasising the urgent need for sustainable development that enhances both the environment and human livelihoods.
Professor Mitchual stated, “Our innovations must be directed toward improving human life without compromising nature. As we build faster systems of communication and transport, we must also ensure we protect the very ecosystems that sustain us.”
Dr. Adams Osman provided an overview of the project’s core objectives: to assess the changes in the hydrological systems of the Greater Amanzule Wetlands, evaluate their impacts on ecosystem services and local livelihoods, and co-develop community-based solutions that support both biodiversity and socio-economic resilience.
Mr. Samuel Obosu, the Planning Officer of the Jomoro Municipal Assembly, emphasised the significance of the project to the district’s future, highlighting the value of the multidisciplinary nature of the project and the stakeholders involved in informing comprehensive policy decisions and community-driven restoration efforts.
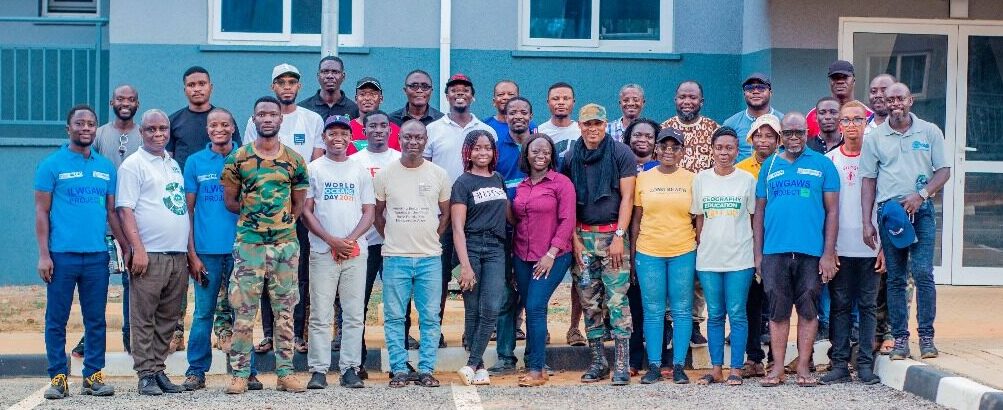
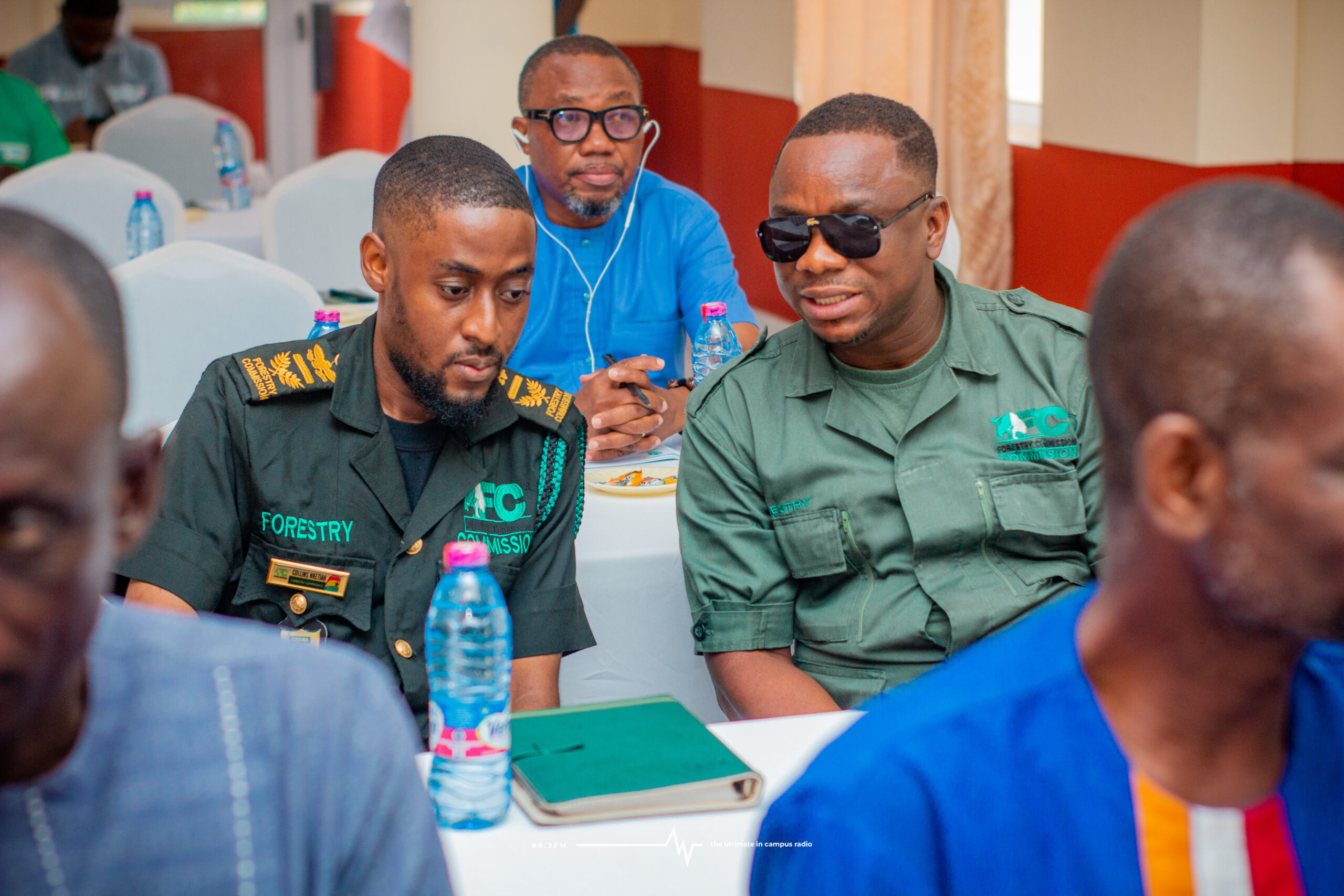
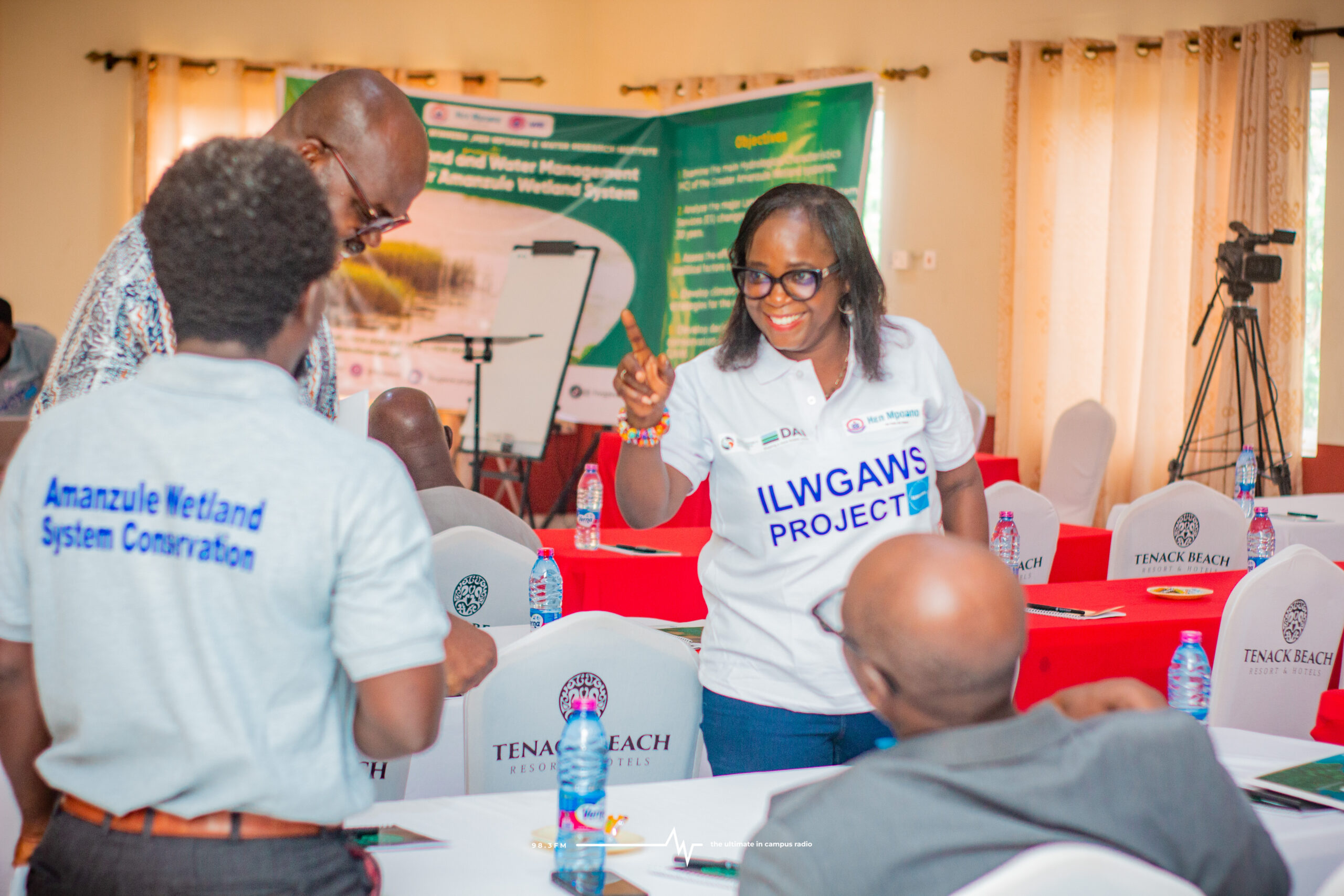
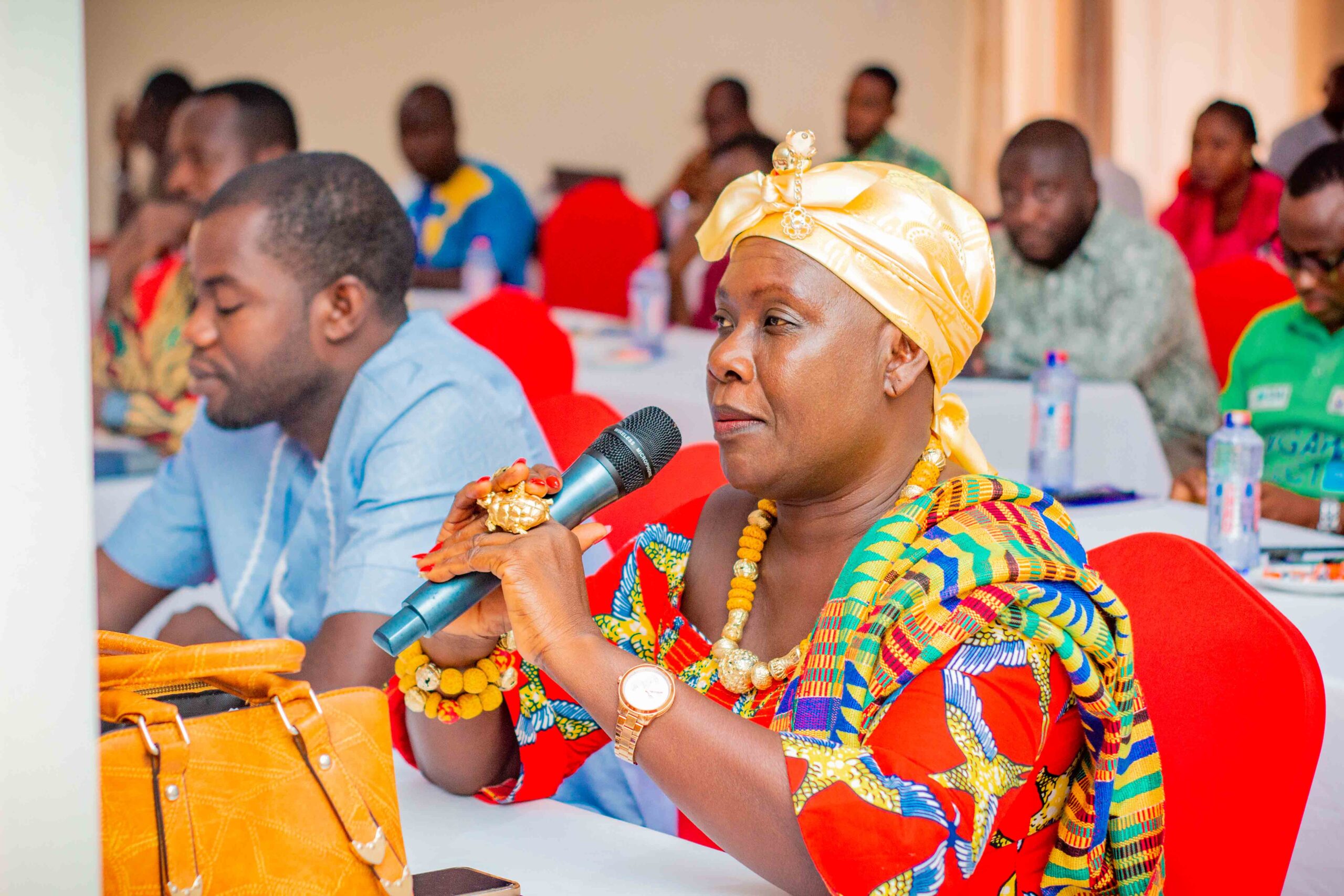
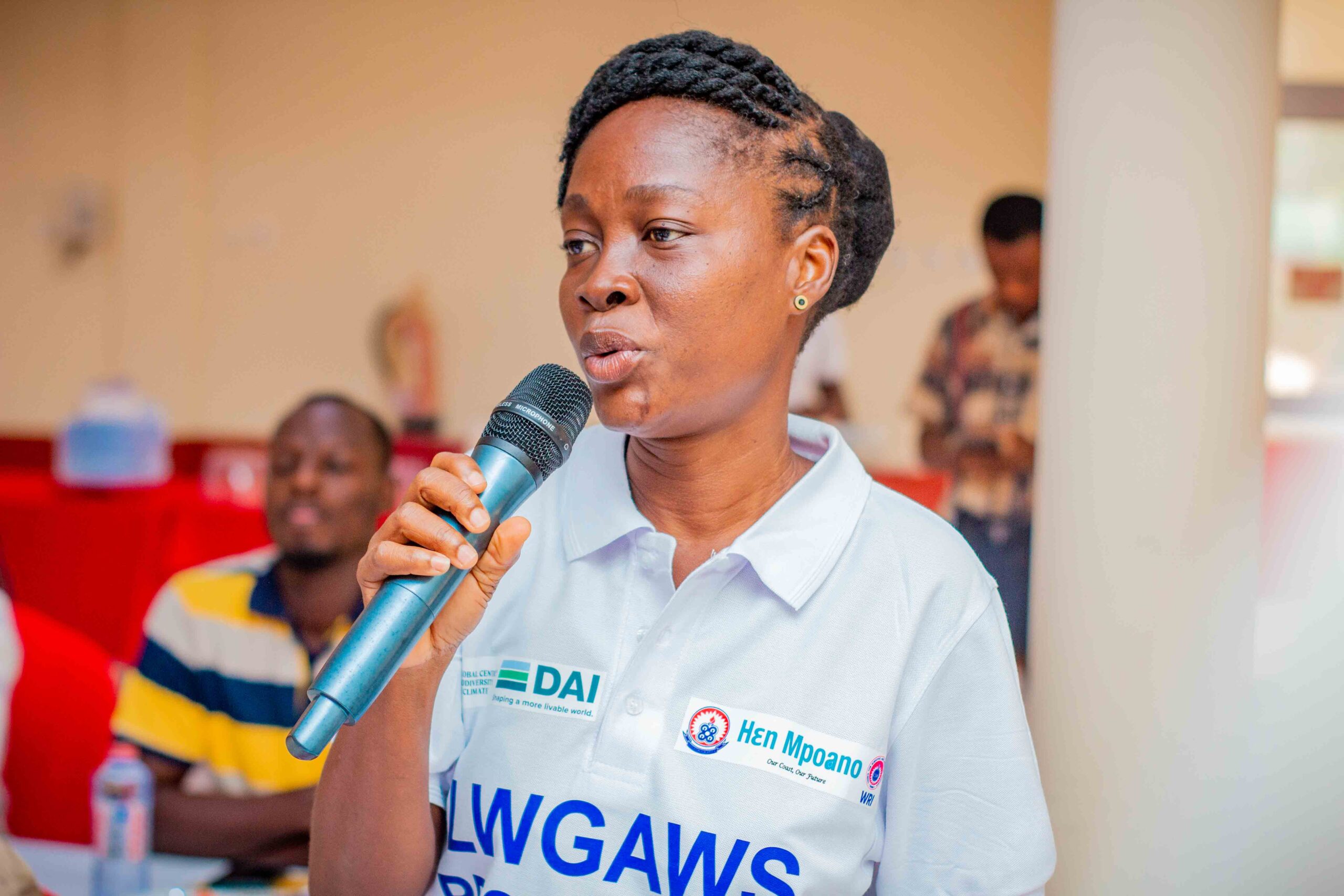
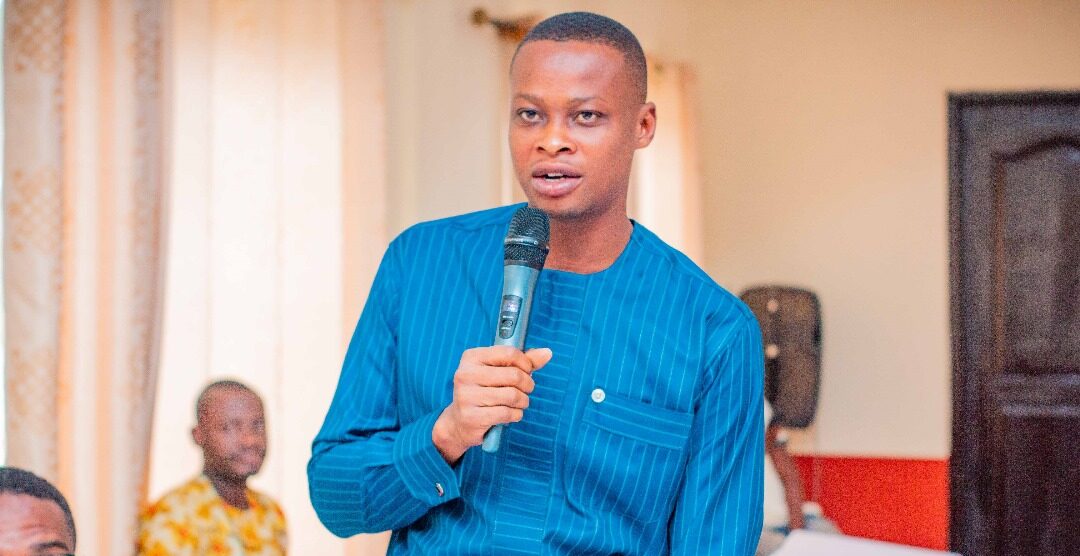
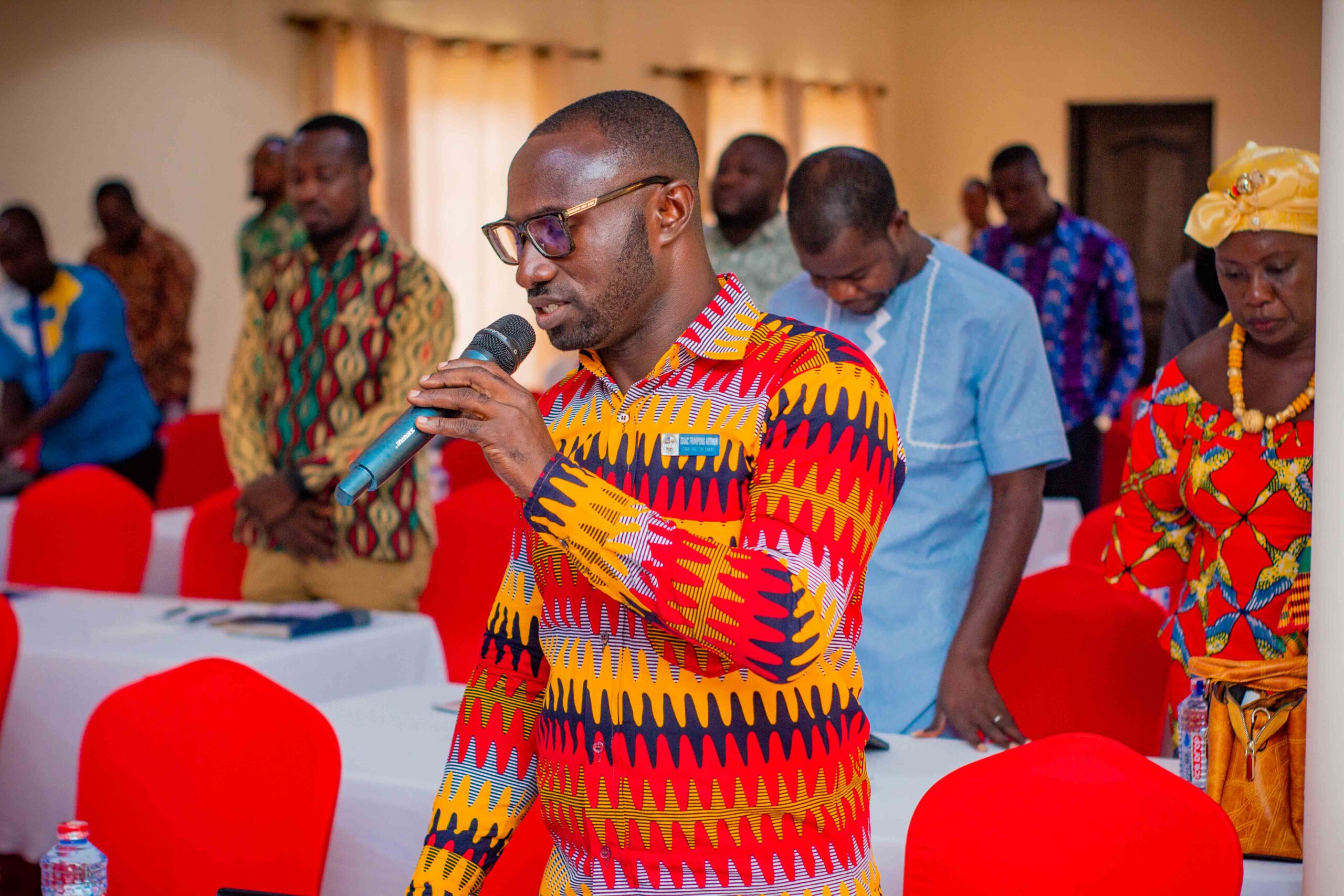





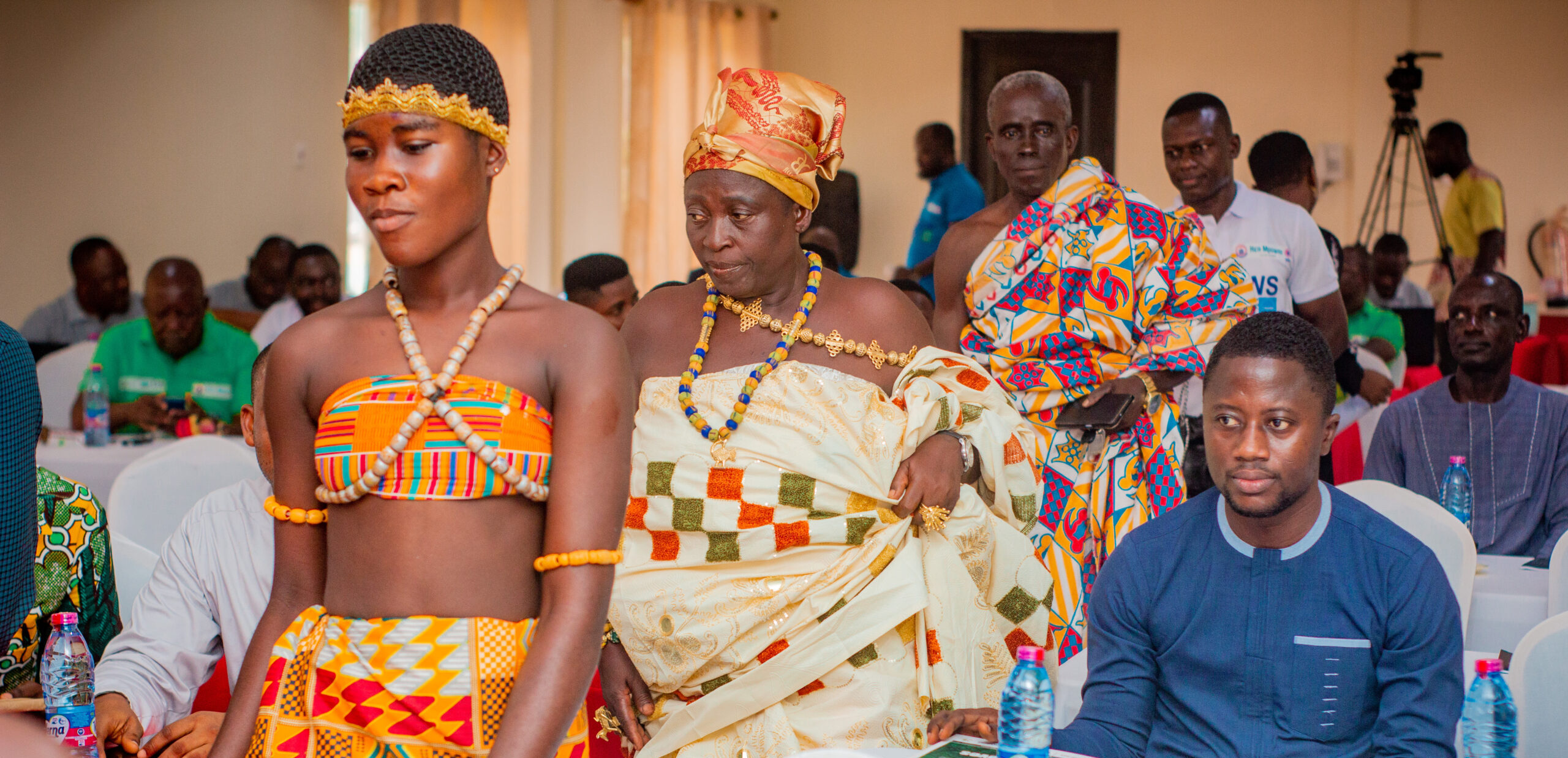


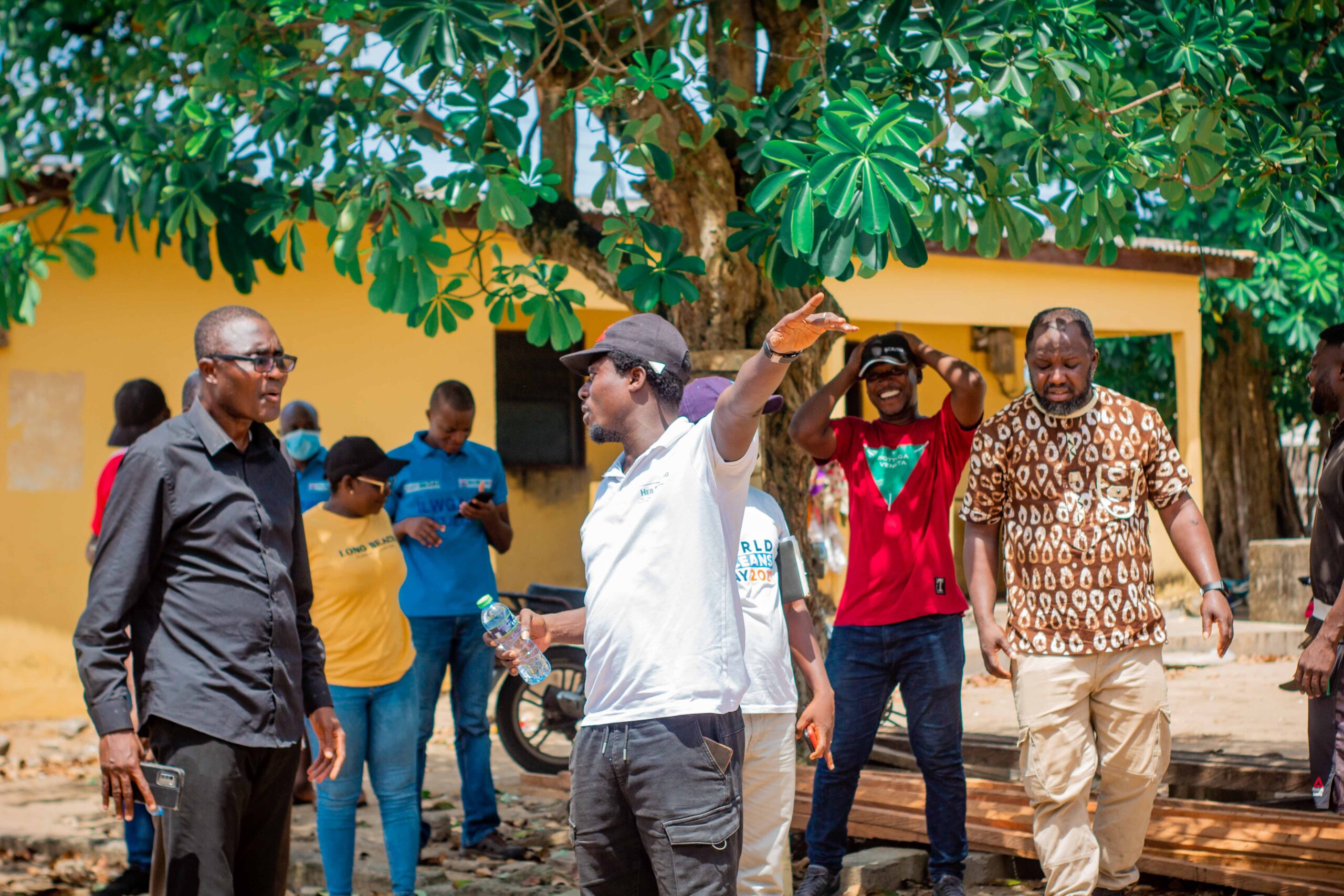
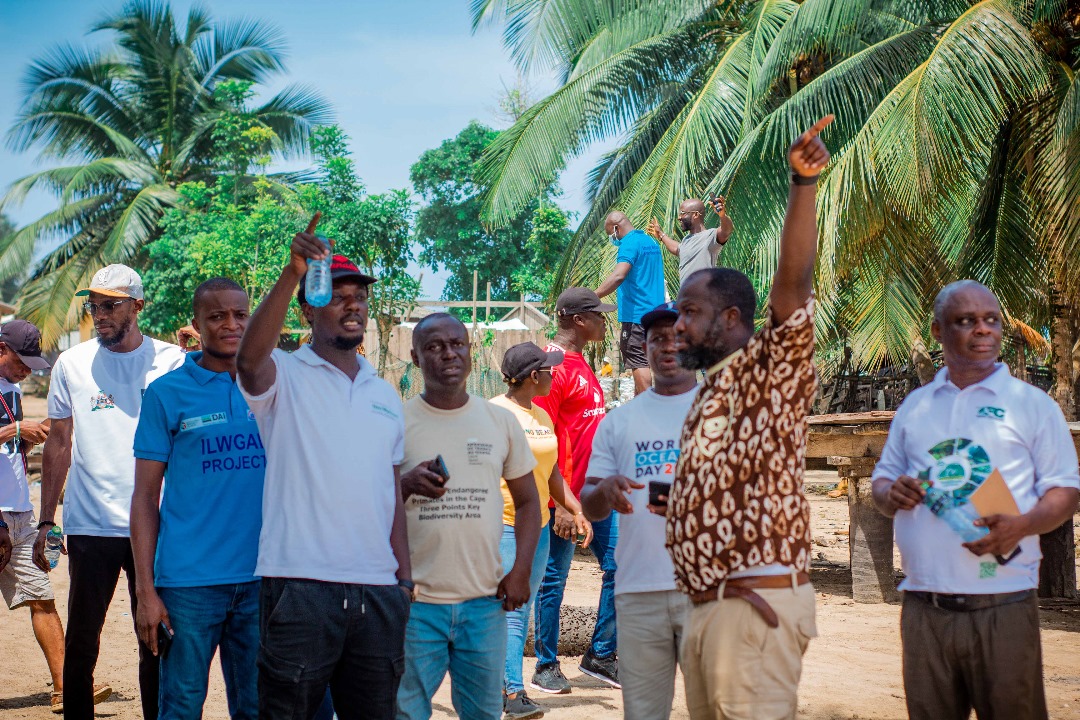
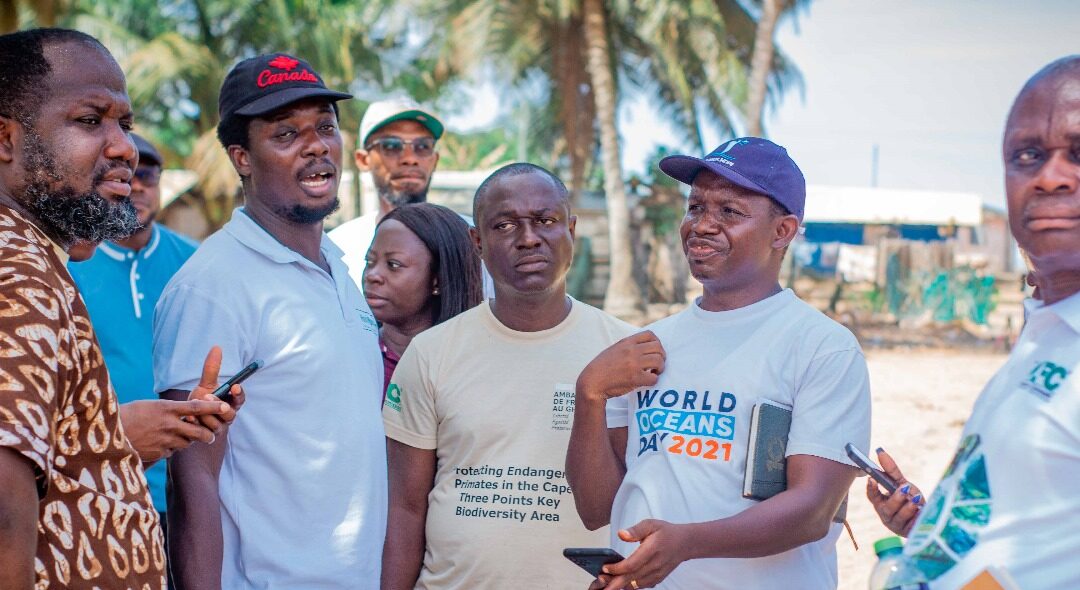
Images show participants at the ILWGAWS launch workshop in the Jomoro Municipality of the Western Region of Ghana. Images courtesy of the ILWGAWS media team.
Reconnaissance Survey: Mapping the Landscape, Understanding the Issues
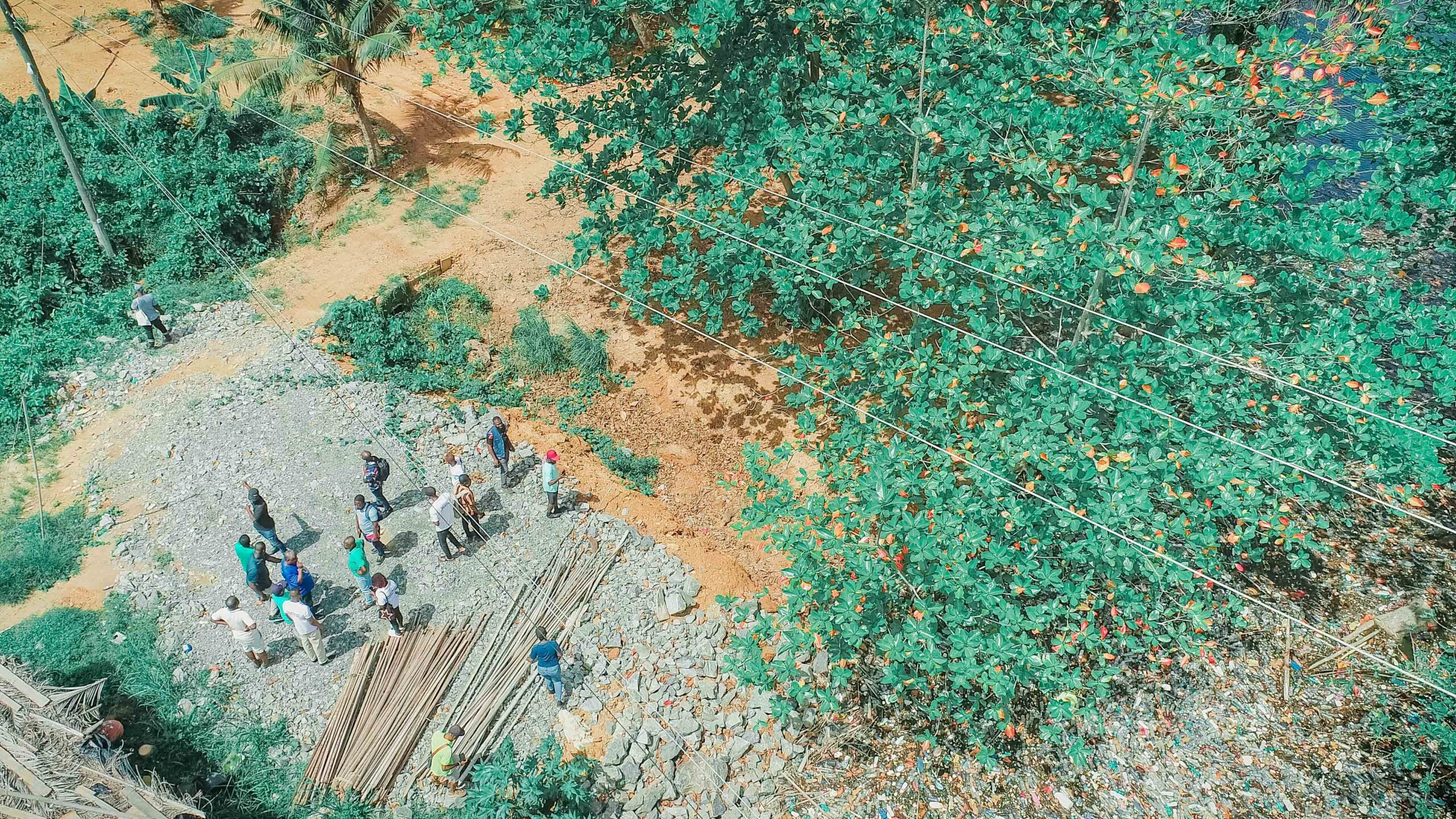
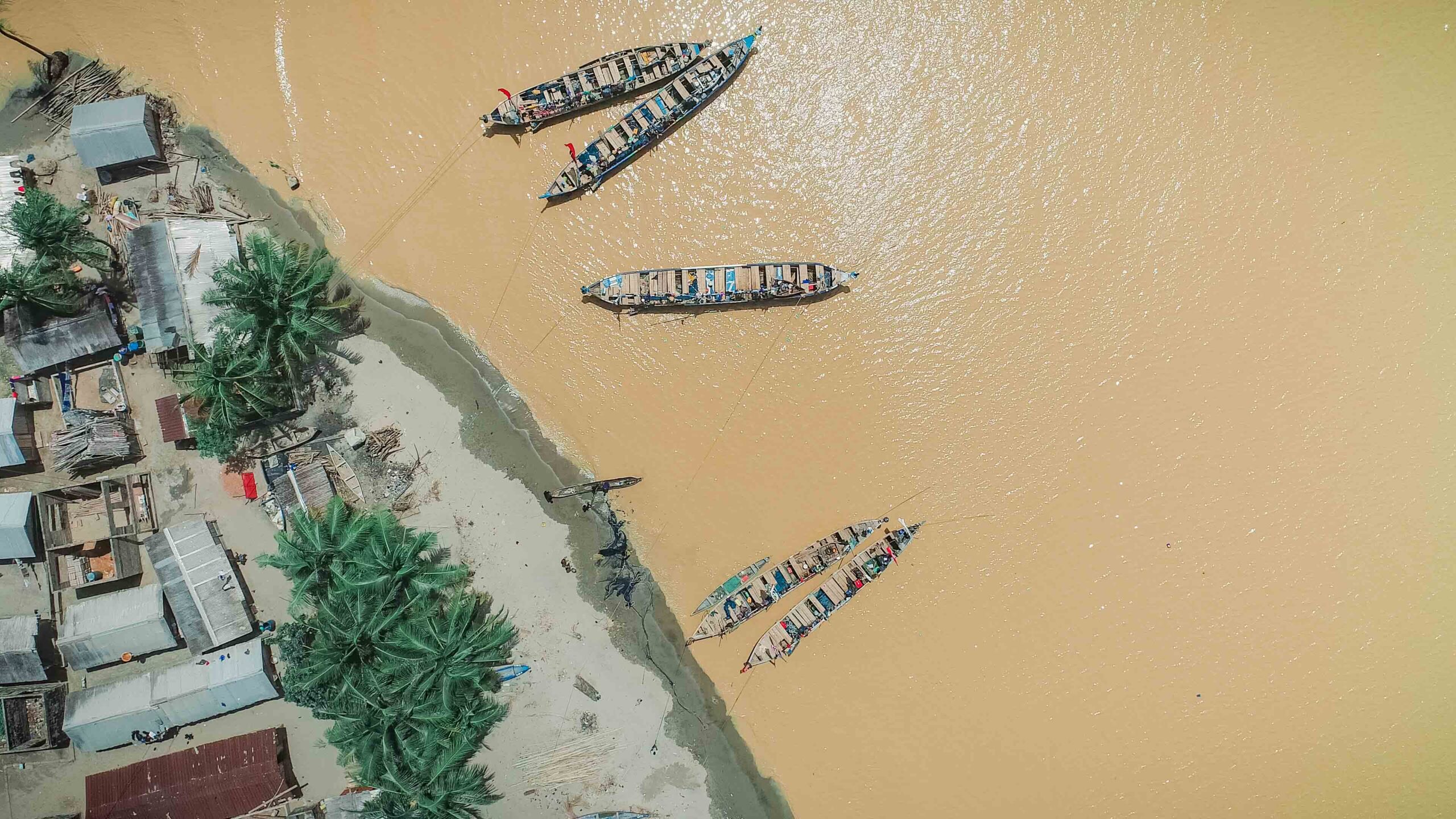
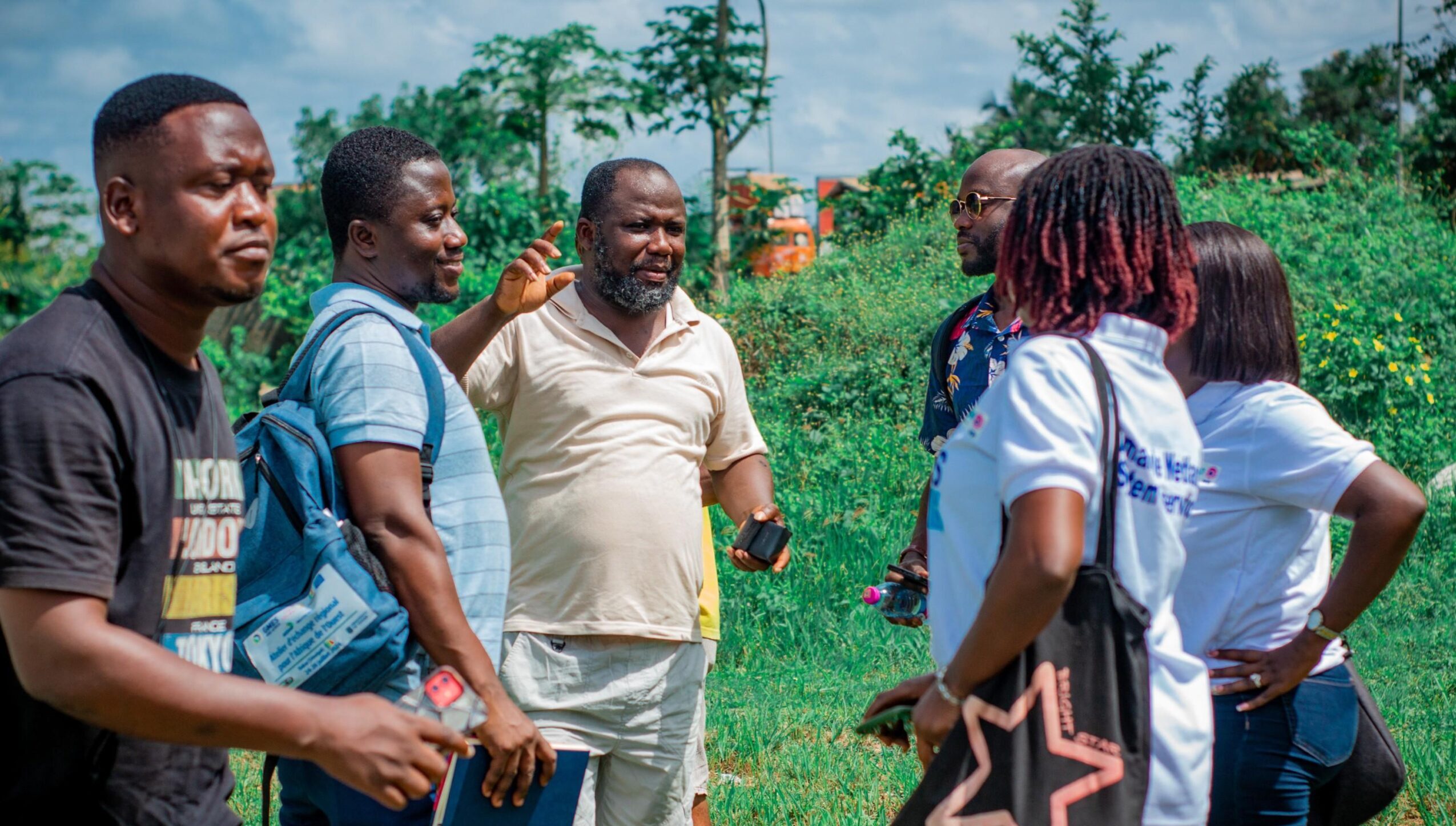
As part of the initial field activities, the ILWGAWS team embarked on a reconnaissance survey across several wetland communities, to assess baseline ecological and socio-economic conditions and identify hotspots for intervention. The survey began with a visit to the Ankobra River estuary, where pollution from illegal mining and waste disposal is severely impacting water quality. At the Asanta community, the team visited a mangrove nursery and conducted a walk-through of the adjacent mangrove forest, documenting signs of degradation and opportunities for restoration. Conversations with local fishers revealed how mangrove loss is affecting fish populations and, by extension, their livelihoods.
At Kamgbunli, the team engaged with traditional authorities and community leaders on the sustainability of fishing practices and their openness to adopting climate-resilient approaches. There were strong expressions of support for the project, particularly regarding mangrove restoration, pollution control, and environmental education. In Old Kabenla Suazo and Ezilinbo, further assessments were conducted, including visits to a lagoon site and the surrounding areas of a naval base under construction. These visits offered insight into the potential land-use conflicts and the need for multi-stakeholder coordination to align development with conservation.
Stakeholder Engagement: Strengthening Local Partnerships
Following the launch, the project team engaged key community leaders and institutional partners in a series of discussions. These engagements focused on identifying existing environmental challenges, possible solutions, refining project objectives and collective responsibilities. Stakeholders expressed concerns about uncontrolled logging, illicit mining, mangrove harvesting, pollution from agrochemicals and plastics, and the impact of infrastructural development on the wetland ecosystem. The dialogue reinforced the project’s commitment to a participatory governance model where communities are not just beneficiaries, but co-implementers of conservation action.
Looking Ahead: Building a Greener Future
The ILWGAWS project is envisioned not as a one-off intervention but as a long-term commitment to ecosystem restoration and climate adaptation. Over the coming weeks, the project will roll out activities in environmental education, hydrological profiling, biodiversity monitoring, mangrove and tree planting, pollution control, and sustainable livelihood training, including beekeeping for local farmers.
Intending to plant 60,000 trees within the Greater Amanzule Wetlands and train communities in sustainable practices, ILWGAWS aims to serve as a model for integrated wetland management in Ghana and beyond. As environmental threats intensify globally, initiatives like ILWGAWS underscore the power of collaboration, science, and community engagement in restoring ecological integrity and improving lives.
The journey has begun, and its success will be shaped by every voice, every tree planted, and every action toward a more resilient coastal ecosystem.